CREATINE MONOHYDRATE: WHY? WHEN? HOW MUCH?
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound that has gained significant attention in the realms of sports nutrition and bodybuilding.
Widely recognised for its potential to enhance physical performance, creatine is one of the most researched and popular dietary supplements available today.
This article delves into what creatine is, its benefits, usage, and potential side effects, offering a thorough understanding of this powerful supplement.
What is Creatine?
Creatine is a nitrogenous organic acid that helps supply energy to cells, particularly muscle cells, through the formation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). It is synthesised in the liver, kidneys, and pancreas from amino acids such as arginine, glycine, and methionine.
While the body produces about 1-2 grams of creatine per day, it can also be obtained from dietary sources, primarily meat and fish, as well as through Creatine Monohydrate supplementation.
How Does Creatine Work?
Creatine's primary role in the body involves the rapid production of ATP, the energy currency of cells. During high-intensity, short-duration exercises like weightlifting or sprinting, ATP is rapidly depleted. Creatine phosphate donates a phosphate group to ADP (adenosine diphosphate) to regenerate ATP, thereby providing a quick and sustained energy boost. This process helps improve performance, increase strength, and delay fatigue.
Creatine Supplementation
Creatine supplementation typically comes in the form of creatine monohydrate, which is the most researched and widely used form of creatine.
The primary goal of creatine supplementation is to increase the body's stores of creatine phosphate, which plays a crucial role in energy production, particularly during short bursts of high-intensity activities like weightlifting and sprinting.
Creatine supplementation is popular among athletes and fitness enthusiasts seeking to enhance their performance, increase muscle mass and strength, improve exercise capacity, and support overall health, but it provides many benefits for the general and ageing population as well.
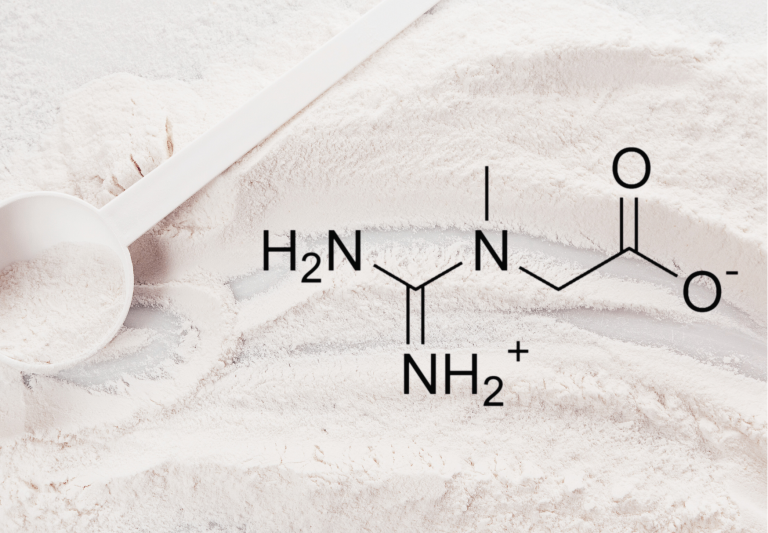
Benefits of Creatine Supplementation:
- Enhanced Athletic Performance: Numerous studies have shown that creatine supplementation can significantly improve strength, power, and exercise performance. Athletes often use creatine to gain an edge in activities that require explosive bursts of energy.
- Muscle Growth: Creatine has been linked to increased muscle mass. It promotes water retention within muscle cells, leading to a temporary increase in size. Additionally, it supports muscle growth by increasing the workload capacity, which leads to greater training adaptations over time.
- Improved Recovery: Creatine helps in reducing muscle cell damage and inflammation following exhaustive exercise, thereby speeding up recovery.
- Cognitive Benefits: Emerging research suggests that creatine may have neuroprotective effects and improve cognitive function, particularly in tasks requiring short-term memory and quick thinking.
- Medical Applications: Creatine is being studied for its potential therapeutic benefits in conditions like neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Parkinson’s and Huntington’s), heart failure, and muscular dystrophy.
How to Use Creatine
Creatine monohydrate is the most common and well-researched form of creatine, known for its efficacy and safety. It is typically mixed with water or a carbohydrate-rich beverage to enhance absorption.
Creatine Monohydrate supplementation typically follows one of two protocols:
Loading Phase:
- This involves taking a high dose of creatine (0.3g/kg of body weight per day, divided into four doses) for 5-7 days. This method saturates the muscle creatine stores quickly.
- Alternatively, one can skip the loading phase and take a consistent 0.03g/kg of body weight daily. While this method takes longer to saturate muscle creatine stores, it is equally effective in the long term.
Maintenance Dose: Loading phase followed by a maintenance dose of 0.03g/kg of body weight per day.
Potential Side Effects
Creatine is considered safe for most people when taken within recommended dosages. However, some users may experience side effects such as:
- Weight Gain: Primarily due to water retention in muscles.
- Digestive Issues: Including stomach cramps, diarrhoea, or bloating, particularly at higher doses.
- Kidney Concerns: While studies show no adverse effects on kidney health in healthy individuals, those with pre-existing kidney conditions should consult a healthcare provider before using creatine.

Tips to Minimise Side Effects:
- Proper Dosage: Start with the recommended dose, and avoid excessive loading doses that may lead to gastrointestinal distress.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to prevent dehydration and minimize muscle cramps and bloating.
- Split Doses: If gastrointestinal issues occur, try splitting the daily dose into smaller portions taken throughout the day.
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: Especially if you have pre-existing medical conditions or concerns.
Effects of Creatine Supplementation on Muscle Building
Creatine supplementation is widely recognised for its powerful effects on muscle building. Here's how it contributes to enhanced muscle growth:
- Increased Muscle Mass: Creatine causes muscle cells to retain more water, leading to a noticeable increase in muscle size and fullness. This volumisation effect provides an immediate visual enhancement and lays the groundwork for further muscle growth.
- Enhanced Protein Synthesis: Creatine supplementation enhances protein synthesis, the process by which muscles repair and grow after exercise. By increasing the efficiency of this process, creatine helps in building muscle more effectively over time.
- Greater Strength and Power: Creatine boosts the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy carrier in cells. During high-intensity exercises like weightlifting, ATP is rapidly consumed. Creatine replenishes ATP stores more quickly, enabling athletes to lift heavier weights and perform more repetitions. This increase in strength and power is crucial for muscle growth.
- Increased Training Volume and Intensity: By delaying the onset of fatigue, creatine allows for longer and more intense workouts. This increased training volume is critical for muscle development. Creatine also aids in quicker recovery between sets and workouts, allowing for more frequent and intense training sessions without the risk of overtraining.
- Hormonal Benefits: Some studies suggest that creatine supplementation can increase levels of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), a hormone that plays a significant role in muscle growth. Elevated IGF-1 levels can further enhance muscle hypertrophy and recovery.
Effects of Creatine Supplementation on Fat Loss
While creatine is primarily known for its muscle-building benefits, it also offers significant advantages for fat loss. Here's how creatine supplementation can support weight loss efforts:
- Preservation of Lean Muscle Mass: During weight loss, it is crucial to maintain lean muscle mass to sustain a healthy metabolic rate. Creatine helps preserve lean muscle tissue, which is important because muscle mass is metabolically active and burns more calories at rest compared to fat tissue. This muscle-sparing effect ensures that weight loss comes primarily from fat stores, not muscle.
- Enhanced Exercise Performance: Creatine improves exercise performance by increasing the availability of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy carrier in cells. This allows individuals to train harder and longer, increasing the total caloric expenditure during workouts. Enhanced performance is particularly beneficial for high-intensity interval training (HIIT), which is known for its effectiveness in burning calories and fat.
- Increased Caloric Expenditure: By enabling more intense and prolonged workouts, creatine supplementation indirectly contributes to greater overall caloric burn. The increased energy output during exercise sessions translates to higher fat loss over time, as more calories are burned both during and after workouts.
- Improved Metabolic Rate: Lean muscle mass significantly influences basal metabolic rate (BMR), the number of calories the body burns at rest. By preserving and potentially increasing muscle mass, creatine helps maintain or boost BMR, aiding in more effective and sustainable weight loss.
- Enhanced Fat Loss: Although creatine does not directly burn fat, the increased workout intensity and volume it supports can lead to greater overall fat loss when combined with a comprehensive exercise and nutrition program. The increased muscle mass also contributes to a higher metabolic rate, further supporting fat loss.
- Reduced Perceived Effort: Creatine can help reduce the perceived effort during exercise, making it easier to perform more intense workouts. This psychological benefit can lead to greater adherence to exercise programs, which is crucial for long-term weight loss success.
Effects of Creatine Supplementation on Cognitive Function
Next to its muscle-building and performance benefits, it’s also gaining recognition for its potential positive effects on cognitive function. Here's an overview of how creatine supplementation can benefit cognitive health:
- Enhanced Brain Energy Metabolism: Creatine plays a crucial role in energy production within cells, including brain cells. It helps increase the availability of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is vital for brain function. Enhanced ATP levels can lead to improved energy metabolism in the brain, supporting cognitive processes that require high energy, such as memory and learning.

- Improved Memory and Learning: Several studies have suggested that creatine supplementation can enhance memory and learning. This is particularly evident in tasks that require short-term memory and quick thinking. By boosting ATP availability, creatine may help the brain process and retain information more efficiently.
- Neuroprotection: Creatine has neuroprotective properties that may protect brain cells from damage. It can help buffer against neurodegenerative processes by maintaining energy levels in brain cells, potentially slowing the progression of diseases such as Parkinson's and Huntington's. Additionally, creatine's antioxidant properties can reduce oxidative stress, further protecting brain cells.
- Enhanced Cognitive Performance Under Stress: Creatine supplementation has been shown to improve cognitive performance in situations of mental fatigue and stress. For example, during prolonged periods of mental effort or sleep deprivation, creatine can help maintain cognitive function by providing a steady supply of energy to the brain.
- Potential Benefits for Depression: Emerging research suggests that creatine may have a role in managing depression. By improving brain energy metabolism and potentially influencing neurotransmitter systems, creatine supplementation could have mood-enhancing effects. Some studies have found that creatine may complement traditional antidepressant treatments, leading to improved outcomes.
- Support for Vegetarians and Vegans: Vegetarians and vegans typically have lower levels of creatine in their bodies since dietary creatine is primarily found in meat and fish. Supplementing with creatine can help boost brain creatine levels in these populations, potentially leading to improvements in cognitive function and mental clarity.
Benefits of Creatine Supplementation for the Ageing Population
Creatine supplementation is not just beneficial for athletes and bodybuilders; it also offers several significant advantages for the elderly.
As we age, maintaining muscle mass, cognitive function, and overall health becomes increasingly important. Here are the key benefits of creatine supplementation for older adults:
Preservation and Enhancement of Muscle Mass and Strength
- Muscle Mass Maintenance: Sarcopenia, the age-related loss of muscle mass and strength, is a common issue among the elderly. Creatine helps in preserving and enhancing muscle mass, which is crucial for maintaining mobility and reducing the risk of falls and fractures.
- Increased Strength: By boosting ATP production, creatine improves muscle strength, allowing older adults to perform daily activities with greater ease and confidence. Enhanced muscle strength contributes to a higher quality of life and greater independence.
Improved Exercise Performance
- Increased Endurance: Creatine supplementation can enhance endurance and exercise capacity, enabling older adults to engage in more prolonged and intense physical activities. This can lead to better overall fitness and health outcomes.
- Better Recovery: Creatine aids in quicker recovery after exercise, reducing muscle soreness and allowing for more frequent and effective training sessions. This is particularly beneficial for older adults who may need more time to recover between activities.
Cognitive Function Support:
- Enhanced Brain Energy Metabolism: Creatine improves energy metabolism in the brain, providing a steady supply of ATP. This can support cognitive functions that require high energy, such as memory and learning.
- Neuroprotection: Creatine has neuroprotective properties that can help protect brain cells from age-related damage. It may slow the progression of neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson's and Alzheimer's by maintaining cellular energy levels and reducing oxidative stress.
- Improved Cognitive Performance: Some studies suggest that creatine supplementation can enhance cognitive performance, particularly in tasks that require short-term memory and quick thinking. This can help older adults maintain mental clarity and cognitive function.

Bone Health
- Increased Bone Density: There is some evidence that creatine, combined with resistance training, can improve bone density. Stronger bones reduce the risk of fractures, which is a significant concern for the elderly.
Conclusion
Creatine stands out as a well-researched and effective supplement for enhancing athletic performance, supporting muscle growth, and potentially offering cognitive benefits.
Its safety profile is robust when used responsibly, making it a valuable addition to many athletes' and fitness enthusiasts' regimens, also provides many benefits to the general and ageing population.
As with any supplement, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before beginning creatine supplementation, especially for those with underlying health conditions.

ALL CONTENTS © FIT BY D 2024. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED..
We need your consent to load the translations
We use a third-party service to translate the website content that may collect data about your activity. Please review the details in the privacy policy and accept the service to view the translations.
